You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Alternate History Combat Aircraft
- Thread starter S. Marlowski
- Start date
-
- Tags
- aircraft helicopter
That one looks a lot like the MiG 1.42/1.44
Got a blank of this one ?
Is this a Dornier do 335 as a Jet?
Kinda reminds me of a Mig-21
Yeah it's a jet version, started out as a simple design, removed the props and added a jet engine but the finished pic reminded me of a Mig as well so I kept making small changes and the final pic really looks a Mig so I think it would've made a good plane.Is this a Dornier do 335 as a Jet?
Kinda reminds me of a Mig-21
In fact of all my alternate designs, I think this one might have actually gotten off the ground.
Still in a little bit of a slump, no new designs, just new paintjobs.Good to see you posting again
Yeah I agree.There's something in this one that screams Luftwaffe '49
Makes me think how well a Mig-336 would work.Yeah it's a jet version, started out as a simple design, removed the props and added a jet engine but the finished pic reminded me of a Mig as well so I kept making small changes and the final pic really looks a Mig so I think it would've made a good plane.
In fact of all my alternate designs, I think this one might have actually gotten off the ground.
We all have those slumpsStill in a little bit of a slump, no new designs, just new paintjobs.
Obviously not 'finished', but I am done with it. Post it or delete it...
Wing and tail are modified from a DH Venom. Engines: Spitfire XIV. Cockpit: P-40
=====
The De Havilland Wasp is a single- or two-seat, multi-role, twin-engines-in-tandem aircraft developed during WW2. It was a low wing monoplane with a distinctive twin-boom tail and tricycle undercarriage. Unusually for wartime aircraft from De Havilland, it was all metal. (The prototypes had some wood in the control surfaces, but these were replaced with metal for production.)
The Wasp I first flew in December 1942, powered by Griffon VI engines. 17 Mark I aircraft were built; these were used for extensive flight testing and later for operational conversion training.
Full-scale production, now of the Griffon 61-powered Mark 2, began in January 1944. Three squadrons -- Nos. 306, 315, and 316 Polish Fighter Squadrons -- were initially selected to operate the Wasp, receiving their planes in March and April[1]. Only 316 Squadron saw combat in the type before D-Day.
Despite their low production numbers (only 595 Wasps of all models were delivered before V-E Day) the plane was popular with its pilots. It was fast, maneuverable, and could carry significant amounts of ordinance in its fighter-bomber role. At least 19 Allied aces (no less than 11 of them Polish) scored some or all of their victories in Wasps.
More than one pilot limped a damaged aircraft back to a friendly airfield on one engine. On 6 September 1944, while on a mission over the Netherlands, the CO of 316 Squadron Major Bohdan Arct, suffered a flak hit which punctured the oil pan of his front engine. The engine soon seized due to oil loss, but Arct was able to make it back across the Channel, landing his wounded mount in a farmer's field. [2]
Notable Wasp pilots:
Pietrzak, Aleksander (316)
Mieczysław Adamek (317)
Janusz Żurakowski (316)
Eugeniusz Horbaczewski (315)
Władysław Gnyś (317)
Jerzy Schmidt (315/306)
Arct, Bohdan Stanislaw (316)
Variants
Wasp I: Griffon VI. 17 produced. Unarmed but ballasted to simulate four 20mm cannons.
Wasp 2: Griffon 61. 210 produced. Four 20mm cannons and two underwing hardpoints for 1000lb of bombs or rockets. Beginning with the 50th aircraft, hardpoints are plumbed for drop tanks.
Wasp 3: 290 produced. Four hardpoints for a total of 2600lb of ordinance. Inboard hardpoints are 'wet'.
Wasp NF Mk 4: 75 produced. A radar pod was carried on the left outboard hardpoint. A radar operator's seat was added to the cockpit by reducing the capacity of the main fuel tank by half.
Wasp NF Mk 5: Griffon 101. 111 produced from 1946. Single-seat model with an American APS-6 radar.
Wasp GR Mk 6: Griffon 105 [3]. 200 produced from 1950. A dedicated ground-attack version with extra armor and reinforced hardpoints. 7000 pound payload.
[1] These squadrons converted from Spitfires to Mustang III (P-51C) about this time OTL. Here they receive somewhat different steeds.
[2] Arct was flying a Mustang III on this day OTL. He suffered an engine failure (or maybe was shot down) and spent the rest of the war in a POW camp.
[3] Griffon 101 with a simplified 2-speed supercharger.
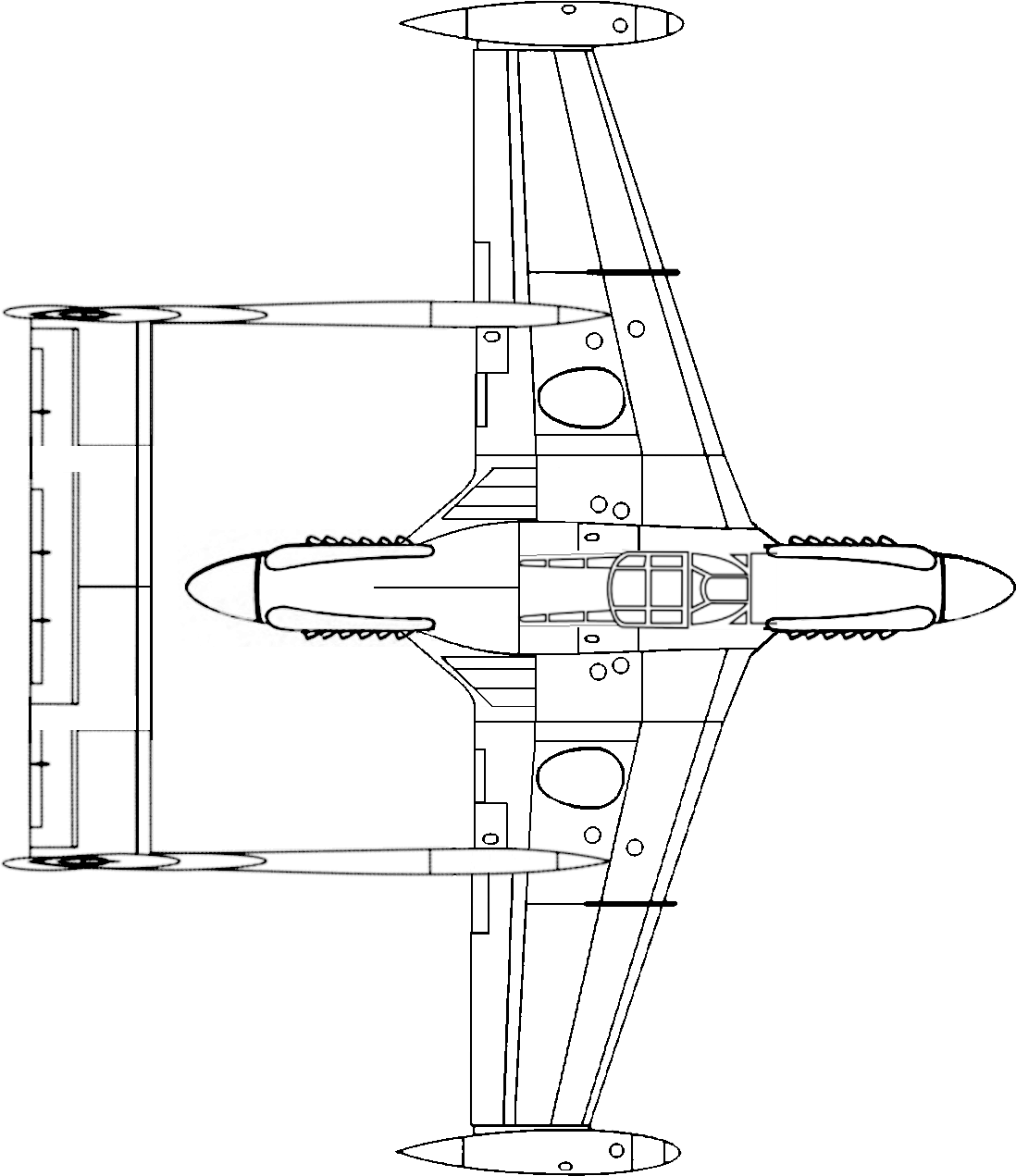
Wing and tail are modified from a DH Venom. Engines: Spitfire XIV. Cockpit: P-40
=====
The De Havilland Wasp is a single- or two-seat, multi-role, twin-engines-in-tandem aircraft developed during WW2. It was a low wing monoplane with a distinctive twin-boom tail and tricycle undercarriage. Unusually for wartime aircraft from De Havilland, it was all metal. (The prototypes had some wood in the control surfaces, but these were replaced with metal for production.)
The Wasp I first flew in December 1942, powered by Griffon VI engines. 17 Mark I aircraft were built; these were used for extensive flight testing and later for operational conversion training.
Full-scale production, now of the Griffon 61-powered Mark 2, began in January 1944. Three squadrons -- Nos. 306, 315, and 316 Polish Fighter Squadrons -- were initially selected to operate the Wasp, receiving their planes in March and April[1]. Only 316 Squadron saw combat in the type before D-Day.
Despite their low production numbers (only 595 Wasps of all models were delivered before V-E Day) the plane was popular with its pilots. It was fast, maneuverable, and could carry significant amounts of ordinance in its fighter-bomber role. At least 19 Allied aces (no less than 11 of them Polish) scored some or all of their victories in Wasps.
More than one pilot limped a damaged aircraft back to a friendly airfield on one engine. On 6 September 1944, while on a mission over the Netherlands, the CO of 316 Squadron Major Bohdan Arct, suffered a flak hit which punctured the oil pan of his front engine. The engine soon seized due to oil loss, but Arct was able to make it back across the Channel, landing his wounded mount in a farmer's field. [2]
Notable Wasp pilots:
Pietrzak, Aleksander (316)
Mieczysław Adamek (317)
Janusz Żurakowski (316)
Eugeniusz Horbaczewski (315)
Władysław Gnyś (317)
Jerzy Schmidt (315/306)
Arct, Bohdan Stanislaw (316)
Variants
Wasp I: Griffon VI. 17 produced. Unarmed but ballasted to simulate four 20mm cannons.
Wasp 2: Griffon 61. 210 produced. Four 20mm cannons and two underwing hardpoints for 1000lb of bombs or rockets. Beginning with the 50th aircraft, hardpoints are plumbed for drop tanks.
Wasp 3: 290 produced. Four hardpoints for a total of 2600lb of ordinance. Inboard hardpoints are 'wet'.
Wasp NF Mk 4: 75 produced. A radar pod was carried on the left outboard hardpoint. A radar operator's seat was added to the cockpit by reducing the capacity of the main fuel tank by half.
Wasp NF Mk 5: Griffon 101. 111 produced from 1946. Single-seat model with an American APS-6 radar.
Wasp GR Mk 6: Griffon 105 [3]. 200 produced from 1950. A dedicated ground-attack version with extra armor and reinforced hardpoints. 7000 pound payload.
[1] These squadrons converted from Spitfires to Mustang III (P-51C) about this time OTL. Here they receive somewhat different steeds.
[2] Arct was flying a Mustang III on this day OTL. He suffered an engine failure (or maybe was shot down) and spent the rest of the war in a POW camp.
[3] Griffon 101 with a simplified 2-speed supercharger.
Share: